Major flaws found in Routers and NAS devices
A total of 125 different security vulnerabilities across 13 small office/home office (SOHO) routers and NAS (Network Attached Storage) devices that have the potential to affect millions of users. In its latest study titled “SOHOpelessly Broken 2.0,” Independent Security Evaluators (ISE) have discovered these vulnerabilities.
SOHO routers and NAS devices tested by the researchers are from the following manufacturers:
Buffalo
Synology
TerraMaster
Zyxel
Drobo
ASUS and its subsidiary Asustor
Seagate
QNAP
Lenovo
Netgear
Xiaomi
Zioncom (TOTOLINK)
As the saying of the security researchers, all of these 13 widely-used devices which were tested by them comprised at least one web application vulnerability that could allow a remote attacker to gain remote shell access or access to the administrative panel of the affected device.
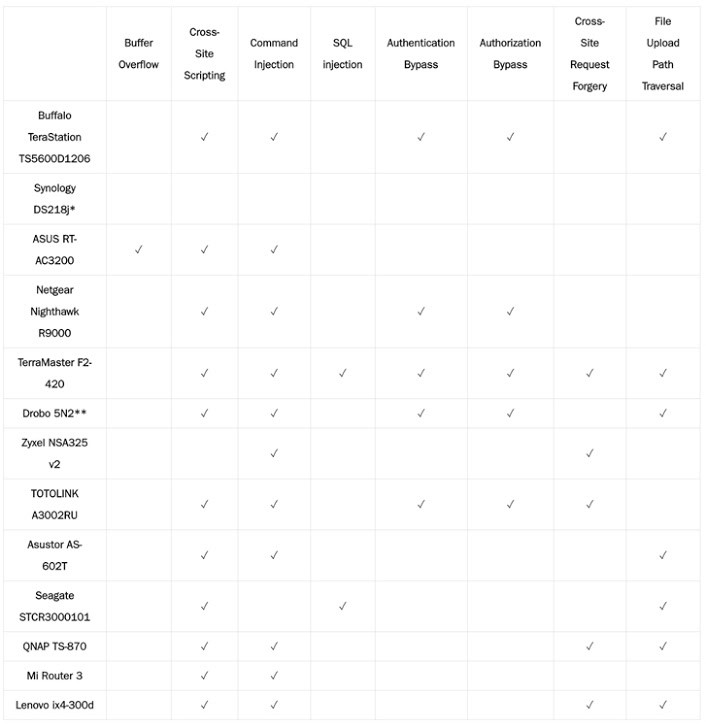
The vulnerabilities discovered include cross-site scripting (XSS), cross-site request forgery (CSRF), buffer overflow, operating system command injection (OS CMDi), authentication bypass, SQL injection (SQLi), and file upload path traversal.
The researchers have successfully confirmed that they obtained root shells on 12 of the devices, allowing them to have complete control over the affected devices, 6 of which contained flaws that would enable attackers to gain full control over a device remotely and without authentication.
The new report, SOHOpelessly Broken 2.0, is a follow-up study of SOHOpelessly Broken 1.0, published by the ISE security firm in 2013, in which they discovered a total 0f 52 vulnerabilities in 13 SOHO routers and NAS devices from vendors including TP-Link, ASUS, and Linksys. Researchers also confirmed that in comparison to SOHOpelessly Broken 1.0, they have found fewer IOT devices that implement security mechanisms like address-space layout randomization (ASLR), functionalities that prevent reverse engineering, and integrity verification mechanisms for HTTP requests. In addition to this, they also said that many things have not changed like the IOT devices still lack basic web application protection features, like anti-CSRF tokens and browser security headers, which can significantly enhance the security position of web applications and the corresponding systems they interact with.
The ISE researchers have reported all the vulnerabilities to the affected device manufacturers to which the vendors have successfully responded and performed security measures to mitigate the vulnerabilities. However, some device manufacturers, including Drobo, Buffalo Americas, and Zioncom Holdings, did not respond to the researchers’ findings.



